Laminated Curved Glass vs. Low-E Glass: Which One is More Energy Efficient?
Laminated Curved Glass vs. Low-E Glass: Which One is More Energy Efficient?
Introduction:
The choice of glass for windows is a critical consideration when it comes to energy efficiency in buildings. Among the various options available in the market, two popular choices are laminated curved glass and low-emissivity (Low-E) glass. Both these glass types exhibit unique features that contribute to energy efficiency. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks of laminated curved glass and Low-E glass, and ultimately determine which one is more energy efficient.
1. Understanding Laminated Curved Glass:
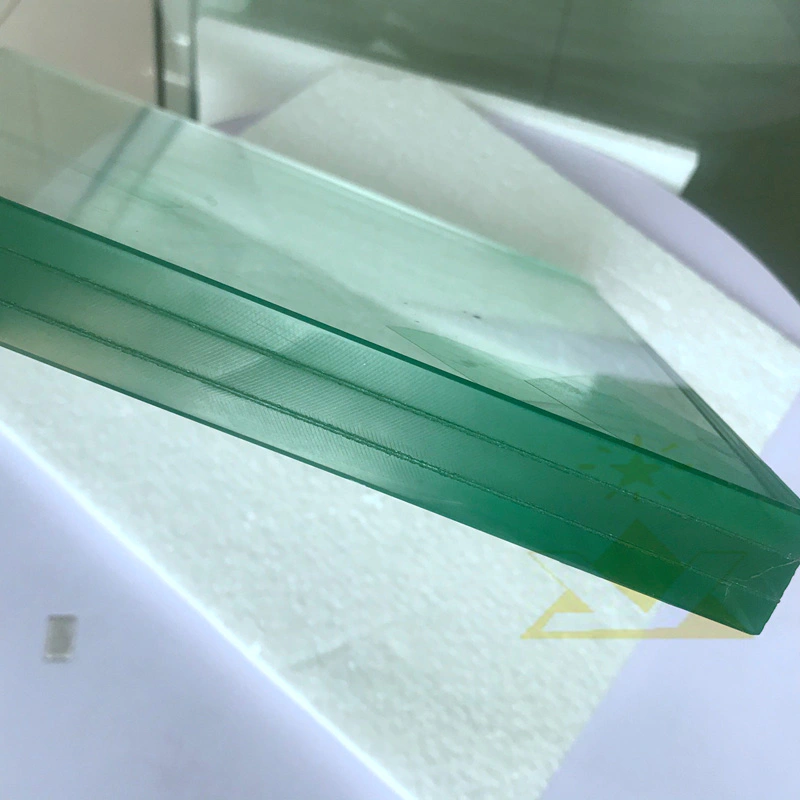
Laminated curved glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded together with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB). This glass type is specially curved to fit architectural designs that require non-linear shapes. Laminated curved glass possesses several advantageous features:
Enhanced Safety: One of the significant advantages of laminated curved glass is its superior safety properties. In the case of breakage, the interlayer holds the shattered glass pieces together, preventing them from causing harm or injuries.
Noise Reduction: Due to its layered structure, laminated curved glass offers better sound insulation compared to other glass types. This feature makes it an appealing choice for buildings in noisy surroundings, such as urban areas or near airports.
UV Protection: Laminated curved glass also provides excellent protection against harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. The interlayer filters out a significant portion of UV radiation, reducing the risk of fading or damage to interior furnishings caused by prolonged exposure to sunlight.
2. Advantages and Limitations of Low-E Glass:
Low-E glass, on the other hand, is a type of glass coated with a microscopically thin layer of metal oxide. This coating helps reduce heat transfer and thereby improves energy efficiency. Low-E glass offers several benefits:
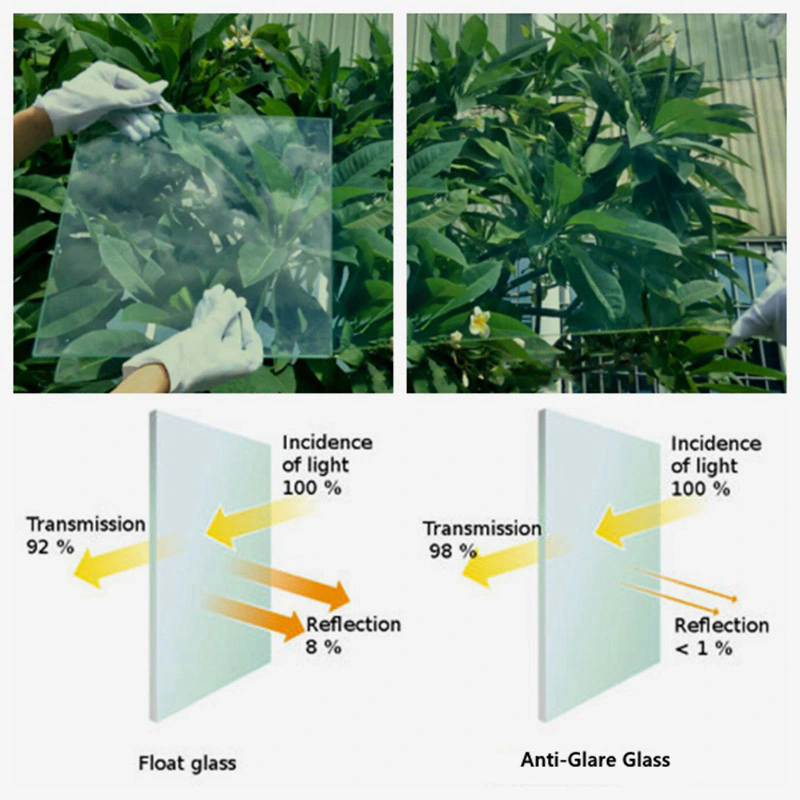
Energy Efficiency: The primary advantage of Low-E glass is its exceptional energy-saving capabilities. The thin metal oxide coating reflects a significant portion of solar heat while allowing visible light to pass through. This prevents heat gain during summer and heat loss during winter, reducing the need for excessive air conditioning or heating.
Optimal Light Transmission: Despite its energy-saving properties, Low-E glass maintains high light transmission, ensuring a well-lit and visually appealing interior environment. It allows natural daylight to illuminate the space while minimizing the penetration of harmful UV rays.
Condensation Control: Another benefit of Low-E glass is its ability to reduce condensation on the glass surface. By reflecting a proportion of heat back into the room, the glass minimizes temperature differences between the interior and exterior, thereby reducing moisture buildup.
However, it is important to note some limitations of Low-E glass:
Cost: Low-E glass is relatively more expensive than standard clear glass or even laminated curved glass. The additional costs associated with the glass and its installation may deter some budget-conscious individuals or builders.
Selection Limitations: Low-E glass is available in different variations, each offering unique performance characteristics. Choosing the right Low-E glass variant for specific climate conditions and building orientations is crucial to optimize energy efficiency. The wide range of options may require expert guidance during selection.
3. Energy Efficiency Comparison:
To compare the energy efficiency of laminated curved glass and Low-E glass, several factors need to be considered:
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC): SHGC measures how well a glass system prevents solar heat from entering a building. Both laminated curved glass and Low-E glass can be customized to achieve specific SHGC values. With expert selection and customized coatings, Low-E glass can offer better SHGC values compared to laminated curved glass.
U-Factor: The U-factor determines the rate at which heat is transferred through the glass. Lower U-factor values indicate better insulation properties. Low-E glass, with its specialized coating, has the potential to achieve lower U-factor values, making it superior in terms of insulation.
Visible Light Transmission (VLT): VLT indicates the amount of visible light that passes through the glass. Laminated curved glass allows ample natural daylight to enter, providing a bright and vibrant indoor environment. Low-E glass also maintains high VLT values but may be slightly lower due to its microscopically thin coating.
Impact Resistance: Laminated curved glass possesses superior impact resistance compared to standard glass or Low-E glass. This characteristic is particularly essential for ensuring safety in areas prone to extreme weather conditions or potential hazards.
4. Application Considerations:
The choice between laminated curved glass and Low-E glass depends on the specific requirements of the building and its location:
Building Orientation: The geographical location and orientation of the building play a significant role in determining the appropriate glass type. In regions with harsh summers, Low-E glass may be more beneficial in reducing heat gain. In contrast, laminated curved glass's resistance to impact makes it more suitable for areas prone to severe weather events, such as hurricanes or storms.
Architectural Design: The design intent of the building should also influence the glass selection. Laminated curved glass offers better flexibility in creating curved architectural elements, adding aesthetic appeal to the structure. Low-E glass, with its diverse options, is suitable for various designs, from modern to traditional.
Budget Considerations: The project budget is an essential factor in the decision-making process. While Low-E glass has long-term energy-saving benefits, it may impose higher upfront costs. Laminated curved glass, although less energy-efficient, can be a viable alternative for those seeking a more affordable option without compromising safety and aesthetics.
Conclusion:
Both laminated curved glass and Low-E glass have distinctive advantages regarding energy efficiency. While laminated curved glass excels in safety, noise reduction, and UV protection, Low-E glass stands out with its energy-saving capabilities, optimal light transmission, and condensation control. The choice between the two ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the building, considering factors like orientation, design, and budget. To achieve the best energy efficiency, it is recommended to consult with industry professionals who can provide expert advice tailored to individual project needs.
Shenzhen Liaoyuan Glass Co., LTD is the largest manufacturer of OEM SERVICE, which is one of the best product manufactured from us.
Shenzhen Liaoyuan Glass Co., LTD supports these goals with a corporate philosophy of adhering to the highest ethical conduct in all its business dealings, treatment of its employees, and social and environmental policies.
The glass panel supplier-type OEM SERVICE is poised to lead the glass panel manufacturer market.
Shenzhen Liaoyuan Glass Co., LTD understands how essential it is to offer ample options, such as OEM SERVICEglass panel supplier to afford high-quality products for customers.
There are many advantages associated with .